Data has become quite precious in today’s digital business world. Most businesses thrive on the data they generate or collect from consumers. With an overwhelming dependence on all kinds of digital consumer data, consumers are increasingly concerned about their privacy and security. It’s when their concerns reached a crescendo that governments all over the world decided to incorporate laws, policies, and regulations that safeguarded their data privacy.
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) is one such regulation introduced by the European Union that aimed at protecting the privacy and personal data of their citizens. It provides guidelines and policies that companies must follow to protect the privacy and personal data of their EU customers. Non-compliance will result in heavy fines and penalties.
CDP, Customer Data, and GDPR
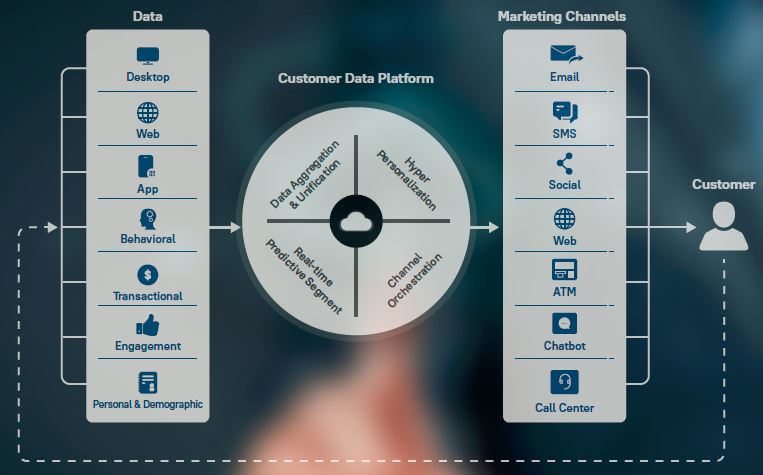
Customer Data Platform (CDP) is a new and innovative martech tool that assists marketers in efficiently managing their customer data. It does this by aggregating and unifying data from various silos and sources to present a single view for each individual user or customer. Using this view, marketers can easily discern valuable insights about each customer and use them to craft personalized campaigns that can help increase digital engagement and conversions.
The concerns that marketers have in a CDP is how does it comply with respect to privacy regulation laws such as GDPR.
A CDP helps in supporting specific GDPR requirements. They are explained as follows:
1. Data Sources Identification
As per the GDPR requirements, all customer data caches must be identified and mapped. A CDP functions primarily by identifying the type of data and their data sources that need to be aggregated and unified.
2. Data Accuracy
CDPs have the capability to create a single unified view of each customer that presents an accurate version of his/her data. This data can be sent back to sources that may have errors. It ensures the downstream propagation of data subject access requests, which is part of the data governance requirements of GDPR.
3. Data Privacy
GDPR requirements state that systems need to be designed with privacy in mind. A CDP adheres to this by centralizing access to the customer’s personal data. It denies systems to directly access each other’s data and only allows them to share it. A CDP can be designed to handle data in such a way that its authorized use and tracking is managed only in the CDP.
4. Data Authority
Marketers can use a CDP to track the authority of how customer data is collected and used. They can assess details such as consents, contracts, legal opinions, authority expiration dates, etc. As the information is readily assembled and available, it can be used to answer questions about how the data is used. CDPs can also be used to make consent adherence simple for downstream systems that receive data that are only GDPR compliant.
How Lemnisk CDP Complies with GDPR
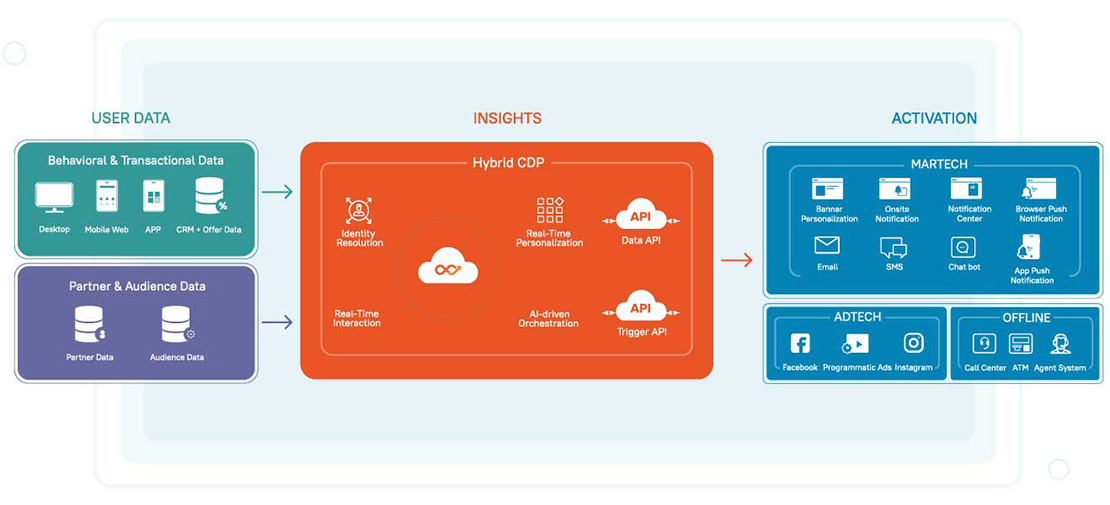
Lemnisk CDP provides an easy to use interface and APIs to Delete and Suppress user data. This is a key requirement to achieve compliance with privacy regulations like GDPR. As part of GDPR, the following rights are available to Data Subjects (end users) with regards to their data stored and managed by Data Controllers (Clients) and Data Processors (Lemnisk):
- Right to erase
- Right to Modify/Rectify
- Right to Access
- Right to Data Suppress (Opt-out)
- Opt-in (Unsuppress)
Use Cases
a) A user can request to Suppress any further data collection from the client’s website. Lemnisk CDP has the capability to receive such suppression requests and process these requests within a stipulated time and provide the status of the request to the client.
b) A user can request to Delete the entire data about this user that is stored on the Lemnisk platform. It can receive such deletion requests and process these requests within 24 hours and provide the status of the request to the client.
Suppress
1. Suppress new data without deleting existing customer data
The data here includes profile as well as events data. Once a suppression request is received for a user, the same can be applied to all the sources. This means that no data (event) about this user is received (processed) at Lemnisk servers across different sources.
2. Suppress new data and delete existing data
All data about the user is deleted from Lemnisk’s managed servers including profile, events, etc. Once the profile is deleted, the platform remembers the identifier and prevents any data from this user across sources to be stored at Lemnisk’s servers.
Delete
Delete existing data without suppressing any new data
All data about the user is deleted from Lemnisk’s managed servers including profile, events, and backup data. The Lemnisk platform is able to receive suppression requests from the client through the Lemnisk GDPR API endpoint.
User Interface to raise and track GDPR requests
Lemnisk CDP can receive suppression requests from the client either through Lemnisk UI or through Lemnisk GDPR Data Suppression API. A suppression request is processed within 24 hours. And once it has been completed, the completion status along with a timestamp is displayed on the UI.
In Conclusion
A CDP’s single unified user view can solve various challenges posed by privacy regulations such as GDPR. Hence, enterprise marketers can definitely proceed with implementing a CDP in their organizations. If they are still concerned, they can ask CDP vendors to present to them their compliance adherence to GDPR and other privacy regulations. This will help them in evaluating each vendor and choose the right one that meets their business goals and objectives.
By Bijoy K.B | Marketing Manager at Lemnisk

Leave a Reply